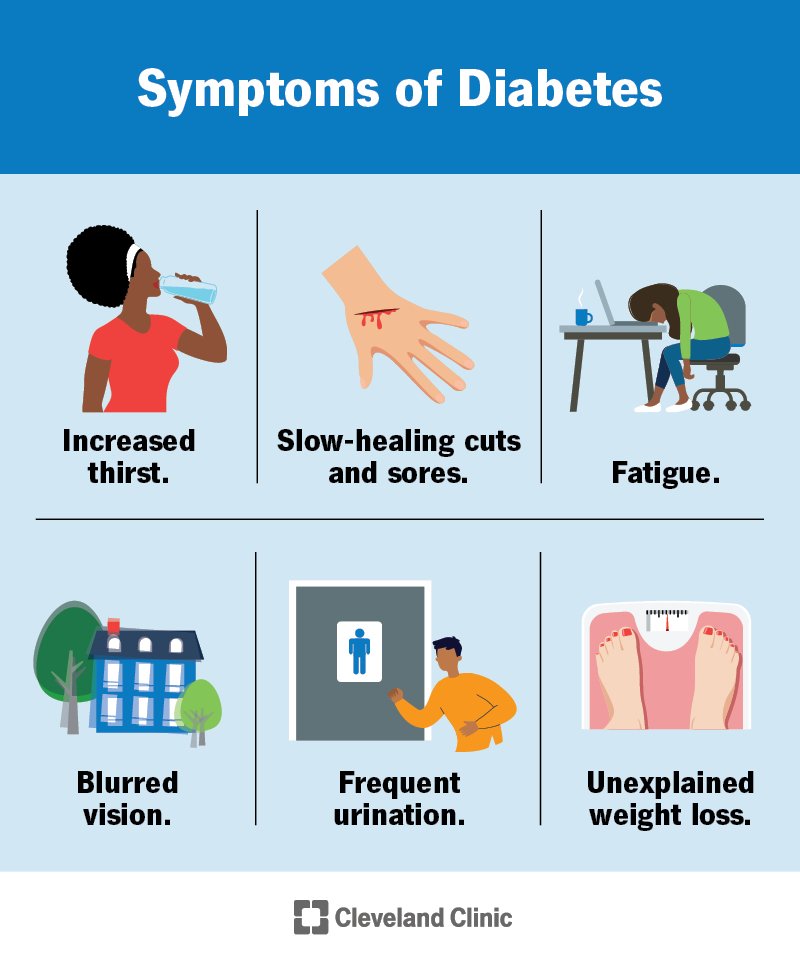
Diabetes happens when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or when it can’t effectively use the insulin it does produce. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar (glucose) levels by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the two main types of diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes:
- Cause:In type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Result:This leads to a complete lack of insulin, causing glucose to build up in the bloodstream instead of entering cells for energy.
Type 2 Diabetes:
- Cause:In type 2 diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin, or the cells become resistant to insulin, meaning they don’t respond properly to the insulin’s signals.
- Result:This leads to high blood sugar levels because glucose can’t enter the cells efficiently.
Other Factors:
- Genetics:A family history of diabetes increases the risk of developing both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
- Lifestyle:Being overweight, obese, and physically inactive can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Other conditions:Conditions like gestational diabetes (occurring during pregnancy), pancreatic damage, or certain hormonal disorders can also lead to diabetes.
In essence, diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by high blood sugar levels due to insufficient insulin production or the body’s inability to use insulin properly.